The Naira Depreciation and Rising Food Prices in Nigeria
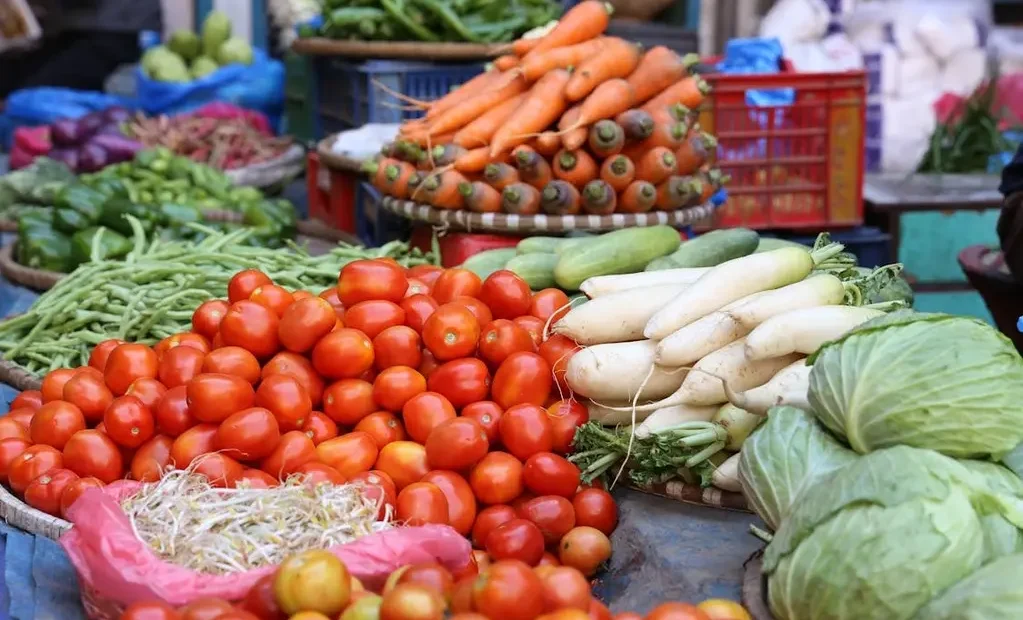

The Nigerian economy is facing significant challenges, with the Naira depreciating to N1,575 per US dollar in the parallel market. This depreciation has led to a dramatic increase in the prices of essential food items such as tomatoes and beans, which have risen by over 300% in just one year, according to the National Bureau of Statistics.
Understanding Naira Depreciation
Naira Depreciation: The value of the Naira, Nigeria’s currency, has significantly dropped compared to the US dollar. In the parallel market, one dollar now costs N1,575. This steep decline in value affects the purchasing power of Nigerians, making it more expensive to buy imported goods and services. Several factors contribute to the Naira’s depreciation. These include reduced foreign exchange reserves, lower oil prices (as oil is Nigeria’s main export), and economic policies that may not adequately support the currency. The demand for foreign currency has outpaced supply, driving up exchange rates.
Impact on Food Prices
Why Prices are Rising: The increase in food prices is due to several reasons:
Import Costs: Many agricultural inputs like fertilizers and machinery are imported. With the Naira depreciating, these inputs become more expensive, increasing the overall cost of production.
Supply Chain Issues: Disruptions in the supply chain, possibly due to economic instability, also contribute to rising prices.
Addressing the rapid depreciation of the Naira and the sharp increase in food prices requires comprehensive economic policies and support for local agriculture. Ensuring economic stability and food security should be top priorities for Nigeria. – Dr. Adeola Adebayo, Economist and Professor at Lagos University.
Effects on Nigerian Households
Increased Cost of Living: With food prices skyrocketing, the cost of living has become much higher for the average Nigerian. Families now spend a larger portion of their income on necessities, leaving less for other needs like education and healthcare.
Food Insecurity: The high cost of food can lead to increased food insecurity. People may not be able to afford nutritious meals, which can affect health and well-being.
Looking Forward
Economic Policies: To address these challenges, the Nigerian government and financial authorities need to implement policies that stabilize the Naira. This could involve diversifying the economy, boosting local production, and improving foreign exchange reserves.
In conclusion, the depreciation of the Naira and the subsequent rise in food prices are pressing issues for the Nigerian economy. Addressing these problems requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on both economic stability and agricultural development.